How Freight Forwarders Optimize China-Europe Shipping Routes
China and Europe are two of the largest and most important trading partners in the world. According to the European Commission, the EU is China’s biggest trading partner, while China is the EU’s second-biggest trading partner. The trade volume between the two regions reached €586 billion in 2020, despite the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Shipping is the main mode of transportation for the trade between China and Europe, accounting for about 90% of the total trade volume. However, shipping is also a complex and challenging process, involving multiple factors such as distance, weather, congestion, regulations, costs, and risks. Therefore, freight forwarders play a vital role in optimizing the shipping routes between China and Europe, ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of the trade.
The significance of China-Europe shipping routes
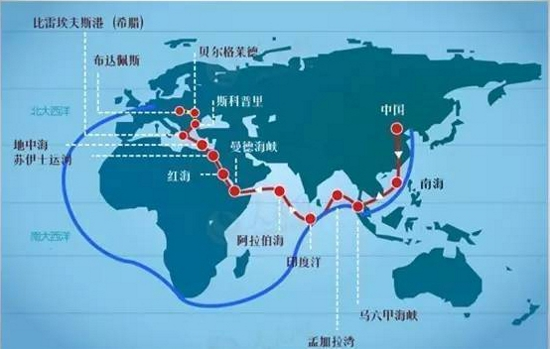
Shipping routes are the paths that ships follow to transport goods from one place to another. They are influenced by various factors such as geography, economics, politics, and technology. Shipping routes can be divided into two types: liner routes and tramp routes. Liner routes are fixed and regular routes that follow a predetermined schedule and serve specific ports. Tramp routes are flexible and irregular routes that depend on the demand and supply of cargo and serve any ports that are convenient.
China-Europe shipping routes are mainly liner routes, as they connect the major ports and markets of the two regions. There are three main types of China-Europe shipping routes: the Northern Sea Route, the Suez Canal Route, and the Belt and Road Initiative Route.
- The Northern Sea Route is the shortest and fastest route between China and Europe, as it passes through the Arctic Ocean and avoids the congested and pirate-infested waters of the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. However, this route is also the most challenging and risky, as it requires ice-breaking vessels, special permits, and high insurance costs. Moreover, this route is only available for a few months a year, depending on the ice conditions.
- The Suez Canal Route is the most traditional and popular route between China and Europe, as it passes through the Suez Canal, which connects the Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. This route is the most economical and reliable, as it offers the lowest freight rates, the highest frequency of services, and the widest network of ports. However, this route is also the most vulnerable and congested, as it faces the threats of piracy, terrorism, political instability, and canal blockages.
- The Belt and Road Initiative Route is the most innovative and diversified route between China and Europe, as it combines sea, land, and rail transportation to create a multi-modal network of corridors and hubs. This route is the most flexible and sustainable, as it offers the shortest transit time, the lowest carbon footprint, and the highest potential for trade and development. However, this route is also the most complex and uncertain, as it involves the coordination of multiple countries, regions, and stakeholders.
Challenges in China-Europe shipping routes
China-Europe shipping routes face various challenges that affect their performance and competitiveness. Some of the main challenges are:
- Capacity imbalance: There is a significant imbalance between the supply and demand of shipping capacity on the China-Europe routes, as the trade volume is much higher from China to Europe than from Europe to China. This results in a shortage of containers, space, and equipment on the westbound leg, and a surplus of empty containers, low utilization, and low freight rates on the eastbound leg.
- Cost escalation: The cost of shipping on the China-Europe routes has increased significantly in recent years, due to various factors such as fuel price fluctuations, environmental regulations, port charges, and market conditions. For example, the average spot rate for a 40-foot container from Shanghai to Rotterdam rose from $1,341 in January 2020 to $8,399 in January 2021, an increase of 526%.
- Service disruption: The service quality and reliability of shipping on the China-Europe routes have deteriorated in recent years, due to various factors such as weather disruptions, port congestion, schedule delays, operational errors, and unforeseen events. For example, the Suez Canal was blocked for six days in March 2021 by a giant container ship, causing a massive backlog of vessels and cargo, and affecting the global supply chain.
How freight forwarders optimize shipping routes

Freight forwarders are intermediaries that arrange the transportation of goods from the origin to the destination on behalf of the shippers. They provide various services such as booking, documentation, consolidation, customs clearance, insurance, and logistics. Freight forwarders play a crucial role in optimizing the shipping routes between China and Europe, as they have the expertise, experience, and network to select the best route, mode, and carrier for each shipment.
Some of the ways that freight forwarders optimize shipping routes are:
- Route selection: Freight forwarders evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each route option, based on the criteria such as distance, transit time, frequency, availability, cost, and risk. They also consider the specific requirements and preferences of the shippers, such as the type, quantity, and value of the cargo, the delivery deadline, and the budget. Freight forwarders then choose the most suitable route for each shipment, balancing the trade-offs between speed, cost, and reliability.
- Mode combination: Freight forwarders combine different modes of transportation, such as sea, land, and rail, to create a multi-modal solution that offers the best of both worlds. For example, freight forwarders can use the sea-rail service that connects the Chinese ports with the European rail terminals, offering a faster and cheaper alternative to the pure sea service. Freight forwarders can also use the land-sea service that connects the Chinese inland cities with the European ports, offering a more convenient and accessible alternative to the pure rail service.
- Carrier negotiation: Freight forwarders negotiate with different carriers, such as shipping lines, rail operators, and trucking companies, to secure the best rates, space, and equipment for each shipment. They also leverage their long-term relationships and contracts with the carriers, to obtain preferential treatment and priority access. Freight forwarders can also use their bargaining power and volume, to obtain discounts and incentives from the carriers.
Technology and tools used in optimizing shipping routes

Technology and tools are essential for freight forwarders to optimize the shipping routes between China and Europe, as they enable them to improve their efficiency, accuracy, and visibility. Some of the technology and tools used by freight forwarders are:
- Digital platforms: Digital platforms are online platforms that connect the freight forwarders with the shippers, carriers, and other stakeholders, allowing them to exchange information, conduct transactions, and manage shipments. Digital platforms can also provide various features such as route comparison, rate quotation, booking confirmation, tracking and tracing, and data analysis.
- Blockchain: Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records and verifies transactions, ensuring their security, transparency, and immutability. Blockchain can also enable smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements that trigger actions based on predefined conditions. Blockchain can help freight forwarders to optimize the shipping routes by reducing the paperwork, enhancing the trust, and facilitating the collaboration among the parties involved.
- Artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that simulates human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision making. Artificial intelligence can help freight forwarders to optimize the shipping routes by providing insights, predictions, and recommendations, based on the data and algorithms. Artificial intelligence can also help freight forwarders to automate and optimize various tasks, such as route planning, mode selection, carrier negotiation, and risk management.
Benefits of optimized shipping routes
Optimized shipping routes can bring various benefits to the freight forwarders, shippers, carriers, and the society at large. Some of the benefits are:
- Cost reduction: Optimized shipping routes can reduce the cost of transportation, by choosing the most economical route, mode, and carrier, and by avoiding the unnecessary expenses, such as demurrage, detention, and penalties. Cost reduction can also increase the profitability and competitiveness of the freight forwarders and shippers.
- Time saving: Optimized shipping routes can save the time of transportation, by choosing the fastest route, mode, and carrier, and by avoiding the delays and disruptions. Time saving can also increase the customer satisfaction and loyalty of the freight forwarders and shippers.
- Carbon emission reduction: Optimized shipping routes can reduce the carbon emission of transportation, by choosing the most environmentally friendly route, mode, and carrier, and by reducing the fuel consumption and waste. Carbon emission reduction can also contribute to the sustainability and social responsibility of the freight forwarders, shippers, and carriers.
Tips for freight forwarders in optimizing shipping routes
Freight forwarders can follow some tips to optimize the shipping routes between China and Europe, such as:
- Stay updated: Freight forwarders should stay updated on the latest trends, developments, and regulations that affect the shipping routes, such as the market demand and supply, the fuel price and surcharge, the environmental and safety standards, and the political and economic situations. Staying updated can help freight forwarders to anticipate and adapt to the changes and challenges in the shipping routes.
- Be proactive: Freight forwarders should be proactive in managing and optimizing the shipping routes, by planning ahead, monitoring the performance, communicating with the parties, and solving the problems. Being proactive can help freight forwarders to improve the efficiency, reliability, and quality of the shipping routes.
For More Information on Shipping to Europe from China contact a professional

Comments
Post a Comment